A-Level Chemistry OCR Notes
3.1.2 Group 2
Download Module Cheatsheet
Google rating
Trustpilot rating
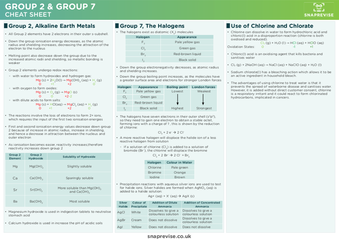
Group 2, Alkaline Earth Metals
- All Group 2 elements have 2 electrons in their outer s-subshell.
- Down the group ionisation energy decreases, as the atomic radius and shielding increases, decreasing the attraction of the electron to the nucleus
- Melting point also decrease down the group due to the increased atomic radii and shielding, so metallic bonding is weaker
- Group 2 elements undergo redox reactions:
- with water to form hydroxides and hydrogen gas:
Mg (s) + 2H2O(l) → Mg(OH)2 (aq) + H2 (g)
0 +1 +2 0
0 +1 +2 0
- With oxygen to form oxides:
Mg (s) + O2 (g) → MgO (s)
0 0 +2 -2
0 0 +2 -2
- with dilute acids to form salts:
Mg (s) + HCl(aq) → MgCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
0 +1 +2 0
0 +1 +2 0
- The reactions involve the loss of electrons to form 2+ ions, which requires the input of the first two ionisation energies
- First and second ionisation energy values decrease down group 2 because of increase in atomic radius, increase in shielding, and hence a decrease in attraction between the nucleus and outer electron
- As ionisation becomes easier, reactivity increases, therefore reactivity increases down group 2
Group 2 Element | Group 2 Hydroxide | Solubility of Hydroxide |
Mg | Mg(OH)2 | Slightly soluble |
Ca | Ca(OH)2 | Sparingly soluble |
Sr | Sr(OH)2 | More soluble than Mg(OH)2 and Ca(OH)2 |
Ba | Ba(OH)2 | Most soluble |
- Magnesium hydroxide is used in indigestion tablets to neutralise stomach acid
- Calcium hydroxide is used in increase the pH of acidic soils
Download as a full cheatsheet for free!

Download Now
Google rating
Trustpilot rating
